ARGs_OAP
The ARGs-OAP (Online Analysis Pipeline) module is designed for rapid ARGs detection from metagenomic data. It uses an integrated structured ARG-database to enhance the accuracy and speed of the analysis.
Stage One
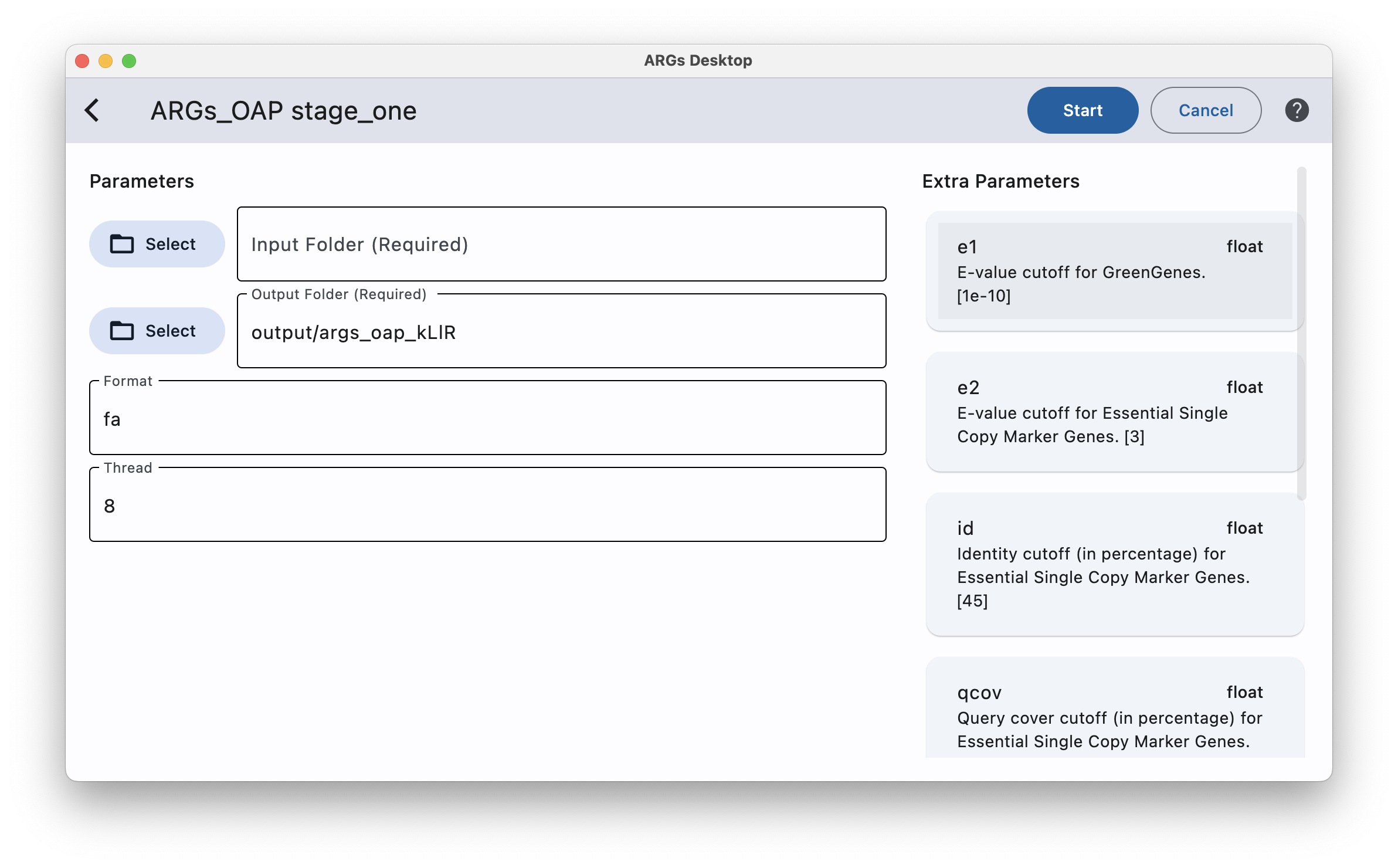 To run stage one of ARGs-OAP, you can optionally enter some extra parameters by simply click the desired parameter card on the right column and then type the value on the left side.
To run stage one of ARGs-OAP, you can optionally enter some extra parameters by simply click the desired parameter card on the right column and then type the value on the left side.
Stage Two
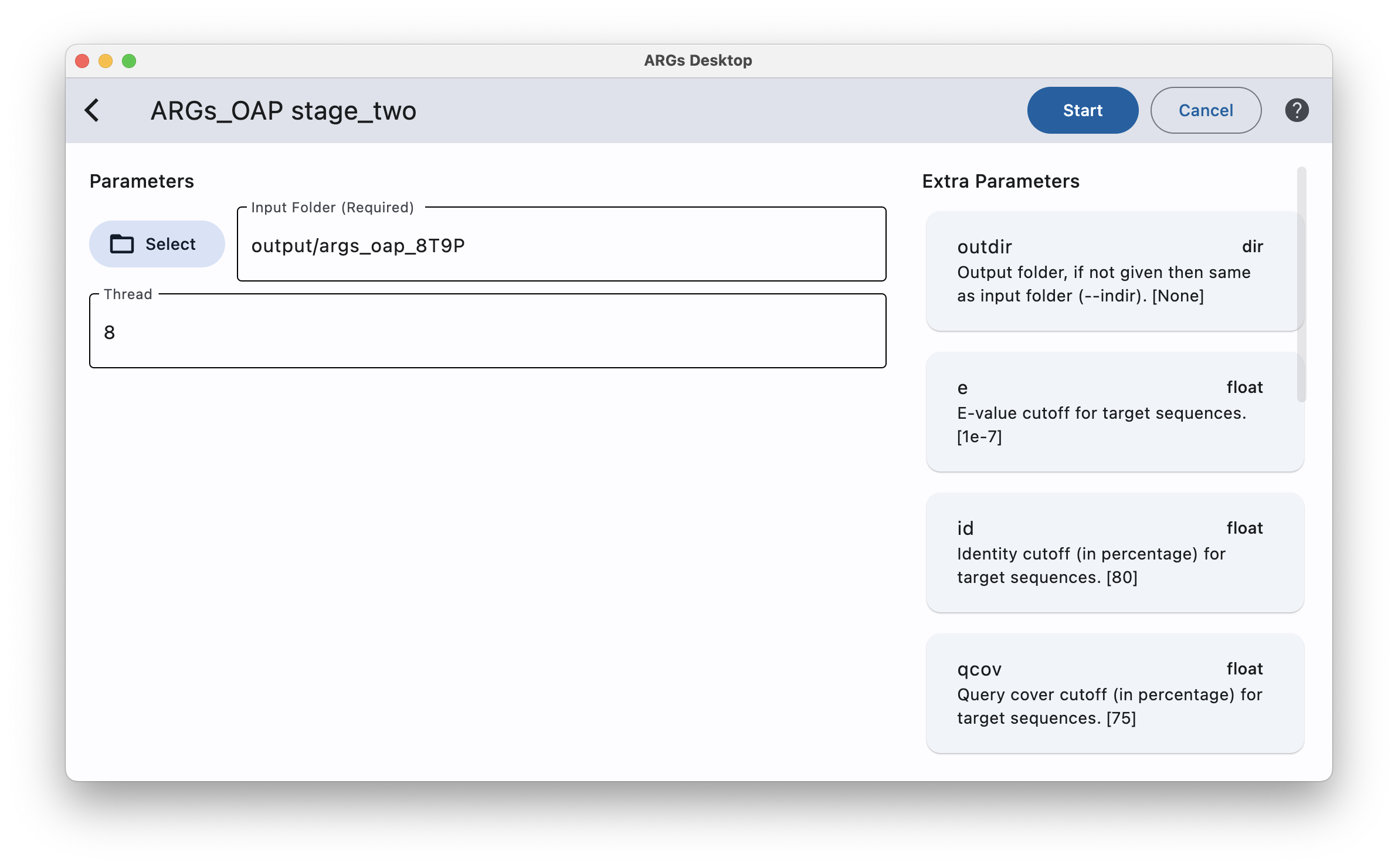 To run stage two of ARGs-OAP, you can optionally enter some extra parameters by simply click the desired parameter card on the right column and then type the value on the left side.
To run stage two of ARGs-OAP, you can optionally enter some extra parameters by simply click the desired parameter card on the right column and then type the value on the left side.
Run All Stages
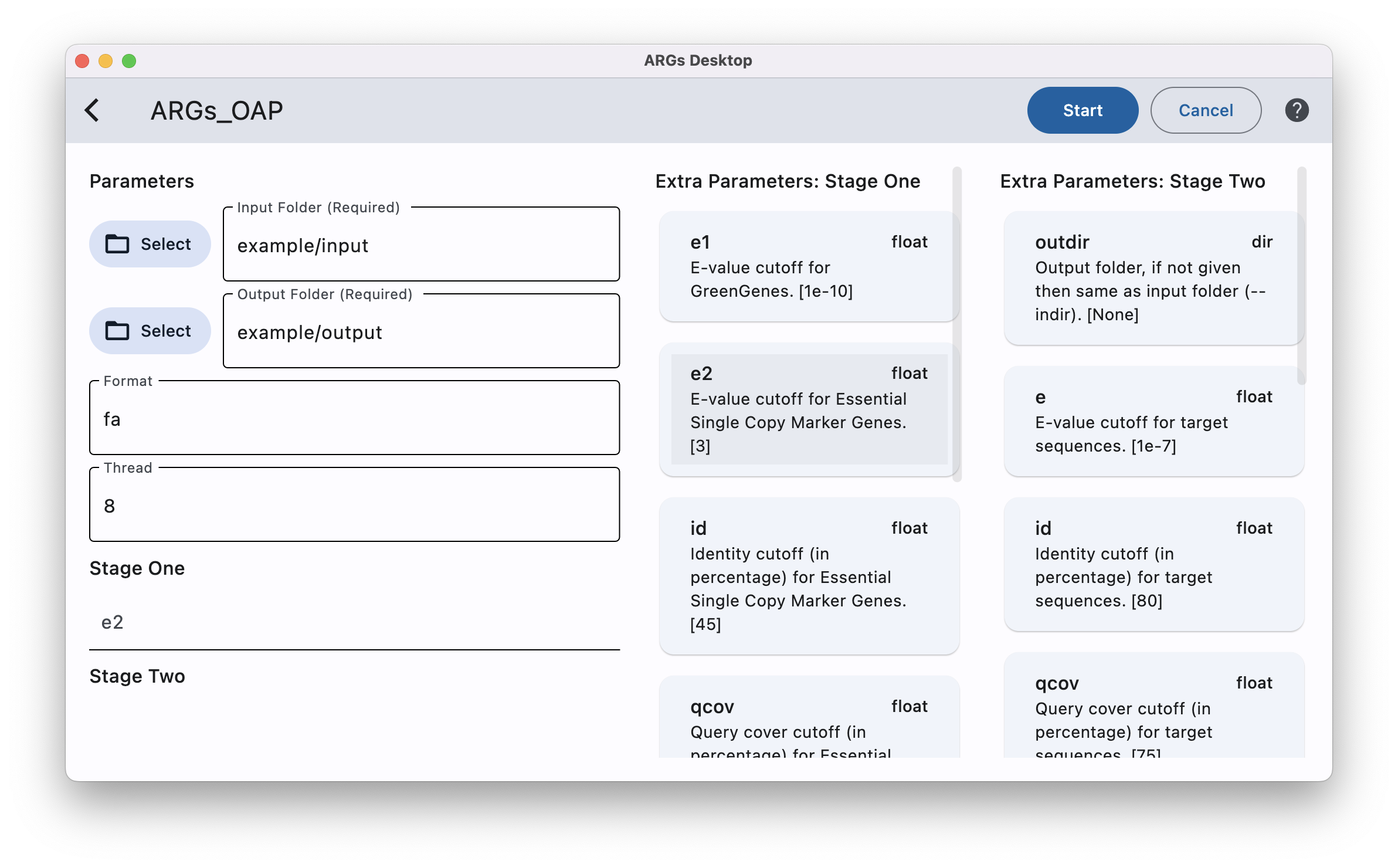 To run all stages of ARGs-OAP, you can optionally enter some extra parameters by simply click the desired parameter card on the right columns and then type the value on the left side. The extra parameters of stage one and stage two can be set seperatelly.
To run all stages of ARGs-OAP, you can optionally enter some extra parameters by simply click the desired parameter card on the right columns and then type the value on the left side. The extra parameters of stage one and stage two can be set seperatelly.
Build Database
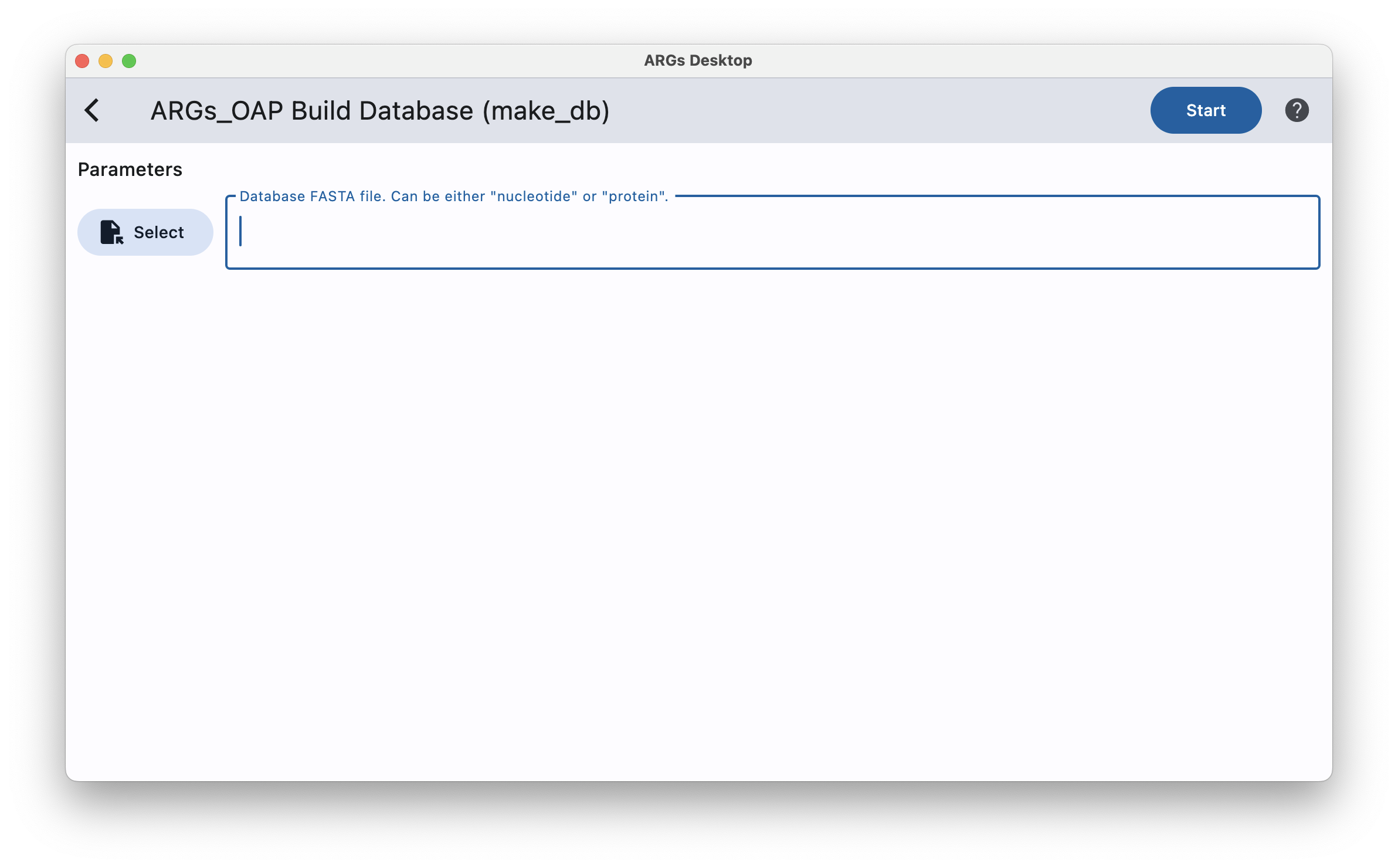
You can build database by selecting target database file. To use the built database on stage one/two, specify the extra parameter database and navigate to target .pdb or .ndb file.
Example
Input: Two example fasta files (100k paired-end reads, 100 bp each) can be found here. The zipped file can be downloaded manually or using wget.
Output: here
About ARGs-OAP (A copy of README from github.com/xinehc/args_oap)
This repository was created by Xiaole Yin (xiaole99) and is currently maintained by Xi Chen (xinhec). The goal is to make args_oap faster, and easier to run.
If you have any questions, please create an issue, or contact Xiaole Yin (yinlele99@gmail.com).
More about the SARG database: https://smile.hku.hk/pipeline/#/Indexing.
Installation
Conda (macOS/Linux):
conda install -c bioconda -c conda-forge args_oap
We suggest to create a new conda environment (here use -n args_oap as an example) to avoid potential conflicts of dependencies:
conda create -n args_oap -c bioconda -c conda-forge args_oap
conda activate args_oap
If your OS satisfies all the dependencies (python>=3.7, diamond>=2.0.15, bwa>=0.7.17, blast>=2.12, samtools>=1.15), then build from source:
git clone https://github.com/xinehc/args_oap.git
cd args_oap
python setup.py install # use python3 if needed
Example
Two example fasta files (100k paired-end reads, 100 bp each) can be found here. The zipped file can be downloaded manually or using wget:
# conda install wget
wget https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/s/pqgftlo24rfc2rd/example.tar.gz
tar -xvf example.tar.gz
cd example
# conda activate args_oap
args_oap stage_one -i input -o output -f fa -t 8
args_oap stage_two -i output -t 8
After stage_one, a metadata.txt file can be found in output. It summarizes the estimated 16S and cell copy numbers in each sample, for example:
| Sample | nRead | n16S | nCell |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAS | 200000 | 8.229297879794053 | 3.145703856125799 |
| SWHAS104 | 200000 | 7.009547807125172 | 3.5116647568418156 |
After stage_two, the normalized ARGs copies per 16S/cells or hits per million reads will be shown in several *_normalized_*.txt files. For example, normalized_16S.type means:
normalized_16S- normalized against 16S rRNA copiestype- Type of ARGs (the hierarchy in SARG is type -> subtype -> gene)
| type | STAS | SWHAS104 |
|---|---|---|
| aminoglycoside | 0.016202273302162947 | 0.06914804847025294 |
| bacitracin | 0.014243756749154238 | 0.0364784305175336 |
| beta_lactam | 0.0 | 0.07424208305458765 |
| macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin | 0.0 | 0.011963015532727394 |
| multidrug | 0.004952224304989356 | 0.096443559902374 |
| mupirocin | 0.0029667248478081566 | 0.004557467877130284 |
| quinolone | 0.14468645528642876 | 0.04399873193528583 |
| sulfonamide | 0.013452071929840085 | 0.06808763199694166 |
| tetracycline | 0.004659396079993178 | 0.04969500656817937 |
Notes
(optional) Single/Paired end files
If you use paired-end files, please make sure the forward/reverse reads end with _1 and _2 or _R1 and _R2 (followed by .format, see -f, .gz optional), otherwise they will not be considered as a single sample. Example for fasta format files (-f fa):
STAS
├── STAS_1.fa
└── STAS_2.fa.gz
SWHAS104
├── SWHAS104_R1.fa
└── SWHAS104_R2.fa.gz
(optional) Customized database/structures
To use customized databases (e.g. mobile genetic elements or heave metal resistant genes), you need to prepare two files:
- nucleotide sequences or amino acid (protein) sequences database (e.g.
database.fasta) - hierarchical structure file (e.g.
structure.txt)
The database should be indexed manually (protein or nucleotide, in fasta):
## protein or nucleotide
args_oap make_db -i database.fasta
The structure file structure.txt should be tab-separated and the first column the sequences ID of database.fasta (please note that the sequence ID cannot contain space, tab and other irregular char such as forward slash). At lease one column (level 1) is required. For the one column (level 1) case, you may construct the structure file using:
echo '>level1' | cat - database.fasta | grep '^>' | cut -d ' ' -f 1 | cut -c2- > structure.txt
One example of the database.fasta and structure.txt is :
database.fasta:
>seq1
ACGT...
>seq2
TGCA...
structure.txt:
level1 level2 level3
seq1 subtype1 type1
seq2 subtype2 type2
To run args_oap with customized database:
args_oap stage_one -i input -o output -f fa -t 8 --database database.fasta
args_oap stage_two -i output -t 8 --database database.fasta --structure1 structure.txt
(optional) Stage two pipeline on Galaxy system and download results
(The online version currently does not support SARG v3.0, please use the local version at this moment.)
Go to http://smile.hku.hk/SARGs and using the module ARG_OAP.
- Using ARG_OAP -> Upload Files module to upload the extracted fasta file and meta_data_online.txt file generated in stage one into Galaxy
- Click ARG_OAP and Ublast_stagetwo, select your uploaded files
- For "Column in Metadata:" chose the column you want to classify your samples (default: 3)
Click Execute and you can find four output files for your information
After a while or so, you will notice that their are four files generated for your information.
File 1 and 2: PcoA figures of your samples and other environment samples generated by ARGs abundance matrix normalization to 16S reads number and cell number
File 3 and 4: Other tabular mother tables which including the profile of ARGs type and sub type information, as long as with other environment samples mother table. File3 results of ARGs abundance normalization against 16S reads number; File 4 results of ARGs abundance normalization against cell number
There are some questions raised by users, please refer to the FAQ for details. To run ARG OAP locally, users should download the source code into local computer system (Unix/Linux). Users can upload the generated files for stage two onto our Galaxy analysis platform (http://smile.hku.hk/SARGs) or use the local version of stage two script.
Changelog
Version 3.2.2 (11. January, 2023)
- Fix naming issue https://github.com/xinehc/args_oap/issues/15.
Version 3.2.1 (22. December, 2022)
- Fix fastq reading bug.
- Rename
scovtocopyin output files.
Version 3.2 (16. October, 2022)
- Simplify interface.
- Remove dependencies on manually entered
metadata.txt. - Support bioconda installation.
Version 3.1.4 (11. October, 2022)
- Remove a duplicated gene ID (ARCH67_P638154538) in KO30 name list.
- Remove gene msrE, mphE and some multidrug genes from database.
- Add RPKM/TPM normalization.
Version 3.1.3 (09. September, 2022)
- Update database to the release version (29082022 short).
- Add parameter
-sfor skipping 16S/cells calculation instageone. - Fix a bug when empty _2 file is being used as input.
Version 3.1.2 (24. August, 2022)
- Support customized database (testing).
- Fix a bug of ppm normalization, now the formula is
#hits * 1e6 / #reads. - Simply stagetwo’s script, add more information for users.
Version 3.1.1 (13. June, 2022)
(If you are expecting results in the unit of ARGs copies per cell (from essential single copy marker genes), this version of fixation won’t affect you.)
- Fix a bug related to the calculation of 16S rDNA copies. Now the numerator is the aligned length instead of read length, and the denominator is the subject length instead of 1432 (the averaged length of 16S rDNA). This will lead to a slight drop of #16S in meta_data_online.txt.
- Fix a bug when estimating 16S rDNA numbers, which causes some 16S to be counted more than one times when multiple high scoring pairs (HSPs) are returned by blastn.
Version 3.1 (09. June, 2022)
- Minor changes to the SARG database (see SARG v3.0-M).
- Update diamond to the latest version (from 0.9.24 to 2.0.15), add a new parameter
-w(query coverage, default 65%) and modify the default parameter of-v(identity, default 40%) in stageone to compensate the difference in USCMG estimation. - Add a
mt_modeswitcher in stagetwo’s blastx to make the pipeline faster when more than 5 cores are available. - Add a logger to make stagetwo’s stdout more clear.
Version 3.0 (04. June, 2022)
- We updated the SARG database and the corresponding structure file to version 3.0 (SARG v3.0-M) .
- We dropped bbmap and usearch from the pipeline, now args_oap support both linux and osx.
- We modified the 16S estimation process by changing minimap2 to bwa + blastn, as minimap2 does not work well for reads that are super short (e.g. below 100 bp, see https://github.com/lh3/minimap2/issues/363#issuecomment-473387994).
- We fixed the version of diamond to 0.9.24 (and python to 3.7.*), as the latest version of diamond (2.0.15) will give ~10% more hits of USCMGs. The sensitivity of the newer version of diamond is under evaluation. We hope to remove this constraint in future updates.
- Bug fixed:
- Fixed a bug that caused the worst hits (instead of the best) to be picked in stagetwo’s blastx when multiple candidates of ARGs can be found.
- Fixed a bug that caused some multi-component ARGs hits to be uncounted in stagetwo’s aggregation process.
- Fixed a bug in stageone that caused USCMG to be slightly overestimated.
- Fixed a bug in stageone that caused parameters
-x-y-vto be ignored.
Notice:
This tools only provide the required scripts for ARGs-OAP 3.0 pipeline
This pipeline is distributed in the hope to achieve the aim of management of antibiotic resistant genes in environment, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.This pipeline is only allowed to be used for non-commercial and academic purpose.
The SARG database is distributed only freely used for academic purpose, any commercial use should require the agreement from the developer team.